shoulder labral tear biceps load test 1 vs 2|shoulder testing algorithm pdf : fabrication In this video, I explain and demonstrate several special tests used in the diagnosis of SLAP tears of the shoulder joint. More specifically, I cover the rationale, interpretation of results,.
webIngresa a Mi Tigo y autogestiona tus servicios móviles y hogar de forma fácil y rápida. Paga tu factura, compra paquetes, mejora tu plan, pospagos, agenda citas, consulta detalles .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB672 Imagens gratuitas de Adrenaline. Imagens sem direitos de autor.
The patient is in the supine position with the shoulder in 120 degrees of elevation and full external rotation, while the elbow is in 90 degrees of flexion, and the forearm in supination. The patient is then asked to flex the elbow as the clinician provides resistance. See moreA positive test is defined as pain experienced during resisted elbow flexion or pain exacerbation during resisted elbow flexion. See moreBiceps Load II Test to Assess SLAP Lesions. The Biceps Load II Test is a common orthopedic test to diagnose superior labral tears from anterior to posterior (SLAP ) lesions in the long .Clinical assessment of physical examination maneuvers for superior labral anterior to posterior lesions. The Surgery Journal, 3 (04), e154-e162. The Biceps Load I Test is a common .
special tests for shoulder pain
shoulder testing algorithm pdf
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive . In this video, I explain and demonstrate several special tests used in the diagnosis of SLAP tears of the shoulder joint. More specifically, I cover the rationale, interpretation of results,.
The biceps load test II is slightly different from the original biceps load test of Kim (biceps load test I) in terms of the position of the arm and definition of a positive test. Rodosky et al.13 .
Biceps Load Test 1. Kim et al (1999) designed the biceps load test to evaluate the integrity ofthe superior glenoid labrum in shoulders with recurrent dislocations. Test. The patient's arm is .
The biceps load test is used to find out the integrity of the superior labrum of the shoulder to see if there is a labral (or SLAP) tear. SLAP Tear stretches & exercises: • SLAP Tear. This Technique Peek Video features Frank Hoeffner, DPT, OCS, demonstrating how to assess for a shoulder labrum tear using the biceps load II test. A positive.Biceps Load Test II. Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of glenohumeral labral tears (SLAP lesion). Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: The examiner brings the patient’s .
The shoulder’s biceps muscle has two attachments: the “short head” is outside of the shoulder joint and rarely causes shoulder problems, while the “long head” travels in front of the shoulder between the rotator cuff tendons and into the .
The active compression test: A new and effective test for diagnosing labral tears and acromioclavicular joint abnormality. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26:610-613. ↑ Owen JM, Boulter T, Walton M, Funk L, Mackenzie TA. Reinterpretation of O'Brien test in posterior labral tears of the .The Biceps Load 2 test is used to identify labral tears (SLAP Lesions) How to Perform Biceps Load 2 Test. Position of Patient: Position the patient in supine. Performance: The examiner will grasp the patient’s wrist and elbow and elevate the arm to 120 degrees of abduction and elbow at 90 degrees of flexion.Fully rotate the arm into external rotation and forearm supination. Biceps Load Test is composed of two parts, Biceps Load Test I and Biceps Load Test II. . while the latter is used for isolated SLAP lesion without anterior shoulder instability. Biceps Load Test I. . Biceps load test: a clinical test for superior labrum anterior and posterior lesions in shoulders with recurrent anterior dislocations. Am J . Synopsis Superior labral tears (SLAP lesions) can pose a significant challenge to orthopaedic surgeons and rehabilitation specialists alike. Although advancement in arthroscopic techniques has enhanced arthroscopic repair of SLAP lesions, the clinical diagnosis of SLAP lesions can still be difficult. There is a variety of etiologic factors associated with SLAP lesions .
This video demonstrates an orthopedic test for superior labrum (SLAP tear) and biceps tendon integrity. Learn how to perform "Biceps Load 2 - Shoulder Special" in order to accurately identify and diagnose SLAP tears and biceps tendon integrity. The glenohumeral joint is composed of the glenoid, humeral head, glenoid labrum, and a surrounding ligamentous complex (figure 1 and figure 2 and figure 3 and figure 4 and figure 5). The labrum is a fibrocartilaginous ring attached to the outer rim of the glenoid that increases the area of contact between the humeral head and glenoid and .the shoulder. The test was named biceps load test II as a counterpart of the original biceps load test for SLAP lesions in shoulders with recurrent anterior disloca-tion. METHODS A prospective study was performed in 127 patients to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy for the biceps load test II. Of the 127 patients, 89 were men and 38
shoulder special tests pdf
Purpose [edit | edit source]. Speed's Test is used to test for superior labral tears or bicipital tendonitis.. Technique [edit | edit source]. To perform the Speed's Test, the examiner places the patient's arm in shoulder flexion, external rotation, full elbow extension, and forearm supination; manual resistance is then applied by the examiner in a downward direction.
Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of glenohumeral labral tears (SLAP lesion). Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: The examiner brings the patient’s shoulder into 120 degrees abduction, maximal external rotation, 90 degrees of elbow flexion and forearm supination.The examiner holds onto the patient's wrist with one hand and stabilizes the elbow . Basic Anatomy and Pathogenesis. The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilagenous structure that runs circumferentially around the rim of the shallow bony glenoid fossa, deepening the socket and acting as a passive stabilizer to prevent humeral head subluxation [2–4].The labrum also serves as an attachment site for capsuloligamentous structures, such as the .
Biceps load test II: a clinical test for SLAP lesions of the shoulder. Arthroscopy 2001 February; 17(2):160-164. ↑ 2.0 2.1 Somerville L, Willits K, Johnson A, Litchfield R, LeBel ME, Moro J, et al. Clinical Assessment of Physical Examination Maneuvers for Superior Labral Anterior to Posterior Lesions. The Surgery Journal. 2017 Oct;03(04):e154 .
The glenoid labrum is integral to shoulder stability and can be difficult to assess clinically. Whilst it is a single anatomical structure, damage to different regions results in very different clinical manifestations. . (Fig. 2). Although the biceps load test I assessed concurrent SLAP injury and instability, the biceps load test II assesses . The Biceps Load II test is a clinical exam that is used to detect Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior (SLAP) lesions in the shoulder. Here are the steps to perform the test: The patient lies on their back on an examination . 1. INTRODUCTION. SLAP lesions of the shoulder are challenging to diagnose by clinical means alone [].Injury occurs from inferior traction on the shoulder, as well as excessive tension on and twisting of the Long Head of Biceps tendon (LHB) at its insertion along the superior labrum that occurs during the cocking motion of throwing [2, 3].These mechanisms of .A sudden onset of posterior shoulder pain indicates a positive test result, regardless of accompanying posterior clunk of the humeral head. Evidence [edit . ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 1. SH Kim et al. A Novel Test for Posteroinferior Labral Lesion .
Biceps load test II (Kim’s test 2) Purpose of Biceps load test II (Kim’s test 2): To detect the superior labral anterior and posterior (SLAP) lesions in the glenohumeral joint (1).. Patient Position: Supine lying. Examiner Position: Standing/Sitting beside the patient’s affected side. Procedure: First, gently grasp the patient’s elbow and wrist on the affected side. This Technique Peek Video features Frank Hoeffner, DPT, OCS, demonstrating how to assess for a shoulder labrum tear using the biceps load II test. A positive. Here I demonstrate for you in this video how to perform the O'Brien's Test and talk about what a positive test is and what it means. 👉MedBridge: Online CEUs.The labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an MRI, CT scan and/or arthroscopy of the shoulder.
The biceps load test II had a sensitivity of 89.7%, a specificity of 96.9%, a positive-predictive value of 92.1%, a negative-predictive value of 95.5%, and a kappa coefficient of 0.815. The abduction and external rotation of the shoulder during the test changes the relative direction of the biceps fiber in a position of oblique angle to the . A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. . posterior load and shift test. patient rests arm at their side. grasp the proximal humerus and apply a posteriorly directed force. . travels within 1 mm . If there is pain located along the bicipital groove the test is positive for biceps tendon pathology. . Axially load the humerus into the glenoid fossa and apply anterior translation forces. Compare to the contralateral side. . positive anterior release is really a "3 in 1" test - if it is positive, apprehension and relocation are also .The biceps load test is used to find out the integrity of the superior labrum of the shoulder to see if there is a labral (or SLAP) tear. With the biceps load test, a positive test doesn’t always mean there is a tear, and a negative doesn’t necessarily mean there isn’t one. To perform the biceps load test, have your patient lie down in .
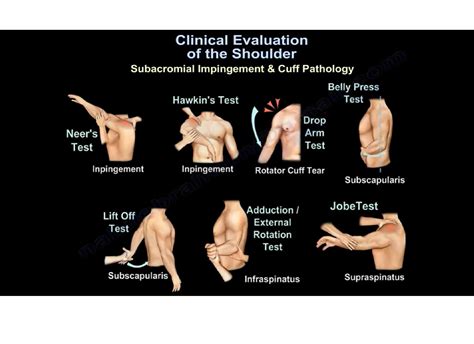
Keywords included “shoulder medical imaging accuracy”, labral tear, shoulder labral tears, special tests, MRI SLAP tear, MRA SLAP tear, sensitivity, specificity, and SLAP tear. A second more focused database search was performed using the keywords Biceps Load Test I, Biceps Load Test II, Active Compression, Speed's Test, Supine Flexion . This type of tear occurs at the front of the upper arm where the biceps tendon connects to the shoulder. Athletes most prone to this injury include baseball pitchers, volleyball, and lacrosse players who engage in high-energy, quick-snap motions over the top of the shoulder which test the structures in the shoulder.
Use Speedtest em todos seus dispositivos com nossos aplic.
shoulder labral tear biceps load test 1 vs 2|shoulder testing algorithm pdf